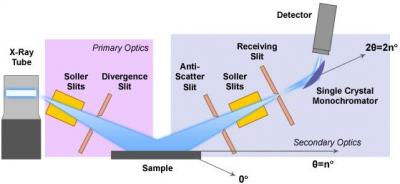
X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) - Techniques. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) is a rapid technique for phase identification and unit cell dimensions of a crystalline material xrd
Xrd
θελω να κερδισω στο κινο
. Learn the fundamental principles, instrumentation, applications, strengths and limitations of XRD from this web page. xrd. X-ray crystallography - Wikipedia xrd. A powder X-ray diffractometer in motion. X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the .. X-ray diffraction (XRD) basics and application xrd. Learn how X-ray diffraction (XRD) works, how to interpret the data, and how to use it for materials characterization. Find useful visualization, literature examples, and works cited resources on this technique that determines a samples composition or crystalline structure. xrd. X-Ray Diffraction - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a highly versatile technique that provides chemical information for elemental analysis as well as for phase analysis. Besides chemical characterization, XRD is extremely useful for stress measurements as well as for texture analysis. Samples to be analyzed using XRD must be crystalline however the technique can provide the degree of crystallinity in polymers. xrd. What is X-Ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD) and How Does it Work?. XRD is a technique to identify materials based on their diffraction pattern. It works by irradiating a material with incident X-rays and measuring the intensities and scattering angles of the X-rays that leave the material
35 év alatti illetékkedvezmény 2019
. XRD can also measure structural properties, such as lattice parameters, strain, grain size, and phase composition. TWI offers XRD analysis services for various industry sectors.. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis Overview - Thermo Fisher Scientific xrd. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a versatile, nondestructive analytical technique thats sensitive to the atomic structure of matter. XRD enables phase identification, quantification, and many more applications used for a diverse array of industrial and research applications xrd. The Thermo Scientific ARL X-ray diffractometers are designed to meet the .. XRD Academy | Thermo Fisher Scientific - US. XRD Basics xrd. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is among the most effective non-destructive tools for identifying and characterizing polycrystalline materials with respect to their crystallography, polymorphic structures, phases and crystallinity changes. By measuring the diffraction angle of a primary X-ray beam according to Braggs Law (λ = 2d sinθ . xrd. X-ray diffraction | Definition, Diagram, Equation, & Facts. X-ray diffraction, phenomenon in which the atoms of a crystal, by virtue of their uniform spacing, cause an interference pattern of the waves present in an incident beam of X-rays.The atomic planes of the crystal act on the X-rays in exactly the same manner as does a uniformly ruled diffraction grating on a beam of light.A beam of X-rays contacts a crystal with an angle of incidence θ.. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) - Overview | Malvern Panalytical xrd. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is the only laboratory technique that non-destructively and accurately obtains information such as chemical composition, crystal structure, crystal orientation, crystallite size, lattice strain, preferred orientation and layer thickness. Materials researchers therefore use XRD to analyze a wide range of materials, from .
felicitari cu ziua de nastere pentru sot si tatic
. Introduction to X-ray Diffraction (XRD) - Chemistry LibreTexts xrd. Interpret XRD diffraction patterns. This module provides an introduction to X-ray Diffraction (XRD), which is a versatile, non-destructive technique that reveals detailed information about the chemical composition and crystallographic structure of materials xrd. It is utilized in a variety of settings ranging from chemistry and materials to geology .. XRD Basics - University of Pennsylvania. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a non-destructive technique for analyzing the structure of materials, primarily at the atomic or molecular level. It works best for materials that are crystalline or partially crystalline (i.e., that have periodic structural order) but is also used to study non-crystalline materials. xrd. X-ray diffraction: instrumentation and applications - PubMed. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful nondestructive technique for characterizing crystalline materials. It provides information on structures, phases, preferred crystal orientations (texture), and other structural parameters, such as average grain size, crystallinity, strain, and crystal defects

pp couple sahabat
. It is based on the constructive interference of monochromatic X-rays and a crystalline sample.. What is X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and What Applications is it Used in?. By Rebecca Ingle, Ph.D Dec 3 2021. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a technique for analyzing the atomic or molecular structure of materials. Crystalline materials are the most analyzed type of material . xrd. XRD - Wikipedia. XRD may refer to: X-ray diffraction, used to study the structure, composition, and physical properties of materials. Extensible Resource Descriptor, an XML format for discovery of metadata about a web resource. Guilty Gear Xrd, a fighting video game. This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title XRD. If an internal link led .
oraculo del guerrero
. XRD - What does XRD stand for? The Free Dictionary. Looking for online definition of XRD or what XRD stands for? XRD is listed in the Worlds most authoritative dictionary of abbreviations and acronyms The Free Dictionary. File extension XRD - Simple tips how to open the XRD file.. Incomplete installation of an application that supports the XRD format; The XRD file which is being opened is infected with an undesirable malware. The computer does not have enough hardware resources to cope with the opening of the XRD file. Drivers of equipment used by the computer to open a XRD file are out of date.. XRD Electronics. ABOUT XRD xrd. PRODUCTS. PARTNER. SERVICE SUPPORT. CONTACT US. Message :. X.R.D will participate the IPC & EMBEDDED EXPO ,2013 xrd. X.R.D Participated in CIGEE Exhibition on June.18 , 2013. XRD passed the Dun & Bradstreet coding certification.. X-Ray Diffraction | SpringerLink
そば湯 tiktok
. X-ray diffraction: The diffraction of X-rays by crystals, producing interference effects (i.e., diffracted beams) at specific angles. The geometry of diffraction is described by Braggs law. Powder diffraction pattern : The diffraction effects (Debye cones, Debye rings) produced by a polycrystalline powder, that is, a large ensemble of small .. Back-to-Basics tutorial: X-ray diffraction of thin films. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is an indispensable tool for characterising thin films of electroceramic materials. For the beginner, however, it can be a daunting technique at first due to the number of operation modes and measurements types, as well as the interpretation of the resultant patterns and scans. In this tutorial article, we provide a foundation for the thin-film engineer/scientist .. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) | SpringerLink. X-ray diffraction: The diffraction of X-rays by crystals, producing interference effects (i.e., diffracted beams) at specific angles. The geometry of diffraction is described by Braggslaw. Powder diffraction pattern: The diffraction effects (Debye cones, Debye rings) produced by apolycrystalline powder, that is, alarge ensemble of small .. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis - Intertek
kartoline per mesuesen
. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD) investigates crystalline material structure, including atomic arrangement, crystallite size, and imperfections. X-ray Diffraction analysis (XRD) is an indispensable tool in both chemical and pharmaceutical research, offering profound insights into the structural properties of crystalline phases.. X Ray Powder Diffraction - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) is also utilized to study the surface property. This analysis will enlighten about the crystallanity or the amorphous nature of the testing materials. For the XRD analysis, very small amount of material is utilized of an order of 0.2 g, which is finely powdered and consistently dispersed on the testing plate.. Minerals | Free Full-Text | X-ray Diffraction Techniques for . - MDPI xrd. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is an important and widely used material characterization technique. With the recent development in material science technology and understanding, various new materials are being developed, which requires upgrading the existing analytical techniques such that emerging intricate problems can be solved xrd. Although XRD is a well-established non-destructive technique, it .. X Ray Diffraction - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics xrd. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is used for the primary characterization of material properties like crystal structure, crystallite size, and strain

κανελλοπουλοσ ξυλεια
. X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF), on the other hand, provides elemental analysis (geochemical analysis) of the same material to complement the mineralogy obtained by XRD

osuba re ma re o
. X-ray diffraction (XRD) | Anton Paar Wiki. X-ray diffraction (XRD) X-ray diffraction is used for the investigation of crystalline materials. All crystalline materials have one thing in common: their components (atoms, ions or molecules) are arranged in a regular manner. This is a necessary requirement for XRD as diffraction can only occur, if X-rays are scattered by a periodic array of .. X-Ray Diffraction - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. Advances in Agronomy. R.A. Viscarra Rossel, . C. Lobsey, in Advances in Agronomy, 2011 2.2.2 X-ray diffractometry. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a nondestructive technique used to acquire detailed information on the mineral composition of the soil. Moore and Reynolds (1997) provide details of the laboratory technique xrd. The use of portable XRD systems and research prototypes are starting to .. PDF 1 Principles of X-ray Diffraction - Wiley-VCH. 3 where ε 0 and c are the vacuum permittivity and velocity of light. The field vector E and wave vector Kare oriented perpendicular to each other as is usual for electro- magnetic waves. The sin term is of significance when the state of polarization is considered for which two extreme cases may arise.. Ray Diffraction - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. XRD is a main technique for the phase identification of materials based on information from unit cell dimensions. An XRD of graphite, graphite oxide, and graphene is shown in Fig. 9.12 [70].A high and sharp diffraction peak of pristine graphite appeared at 2θ = 26.6 degrees xrd. After pristine graphite oxidization, the peak shifted to 13.9 degrees, resulting from the existence of oxygen molecules .. X-Ray Diffraction: Instrumentation and Applications. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful nondestructive technique for characterizing crystalline materials. It provides information on structures, phases, preferred crystal orientations (texture), and other structural parameters, such as average grain size, crystallinity, strain, and crystal defects.. X-ray Diffraction XRD Services | EAG Laboratories



. Yadis became the service discovery format for. A common discovery service for both URLs and XRIs proved so useful that in November 2007 the XRI Resolution 2.0 specification formally added the URL-based method .. X-Ray Diffraction for Determining Atomic and Molecular Structure . - JoVE. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a technique used in materials science for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a material. This is done by irradiating a sample of the material with incident X-rays and then measuring the intensities and scattering angles of the X-rays that are scattered by the material. The intensity of the scattered X .. XRD Literature | X-ray Diffraction SEF. Introduction to XRD, specimen preparation, and lab practices (primarily for clay minerals) US Geological Survey. CCP14. Collection of Free Software and Tutorials for Academia xrd. Jeremy Cockcroft, et al xrd. Symmetry and Space Groups. Excellent Online Tutorial Covering Space Groups in Crystallography xrd. Bruce Foxman xrd. Lab Manual for X-Ray Powder Diffraction. X-ray Diffraction - UGA. The XRD powder method relies on principle that all possible crystallographic orientations are presented to the beam. This concept is known a random orientation xrd. If there is a bias of orientations of one or more particular crystallographic plane, then this is known a preferred orientation. ..